This comprehensive guide is designed for operators and fleet managers using Kales Tipper Semi Trailers. From understanding the advanced hydraulic tipping system to mastering safe unloading procedures and performing routine maintenance, this manual ensures maximum operational efficiency, safety, and longevity for your heavy-duty transport equipment.
1. Choosing the Right Kales Tipper: Rear vs. Side Tipping Trailer
Selecting the correct unloading method is crucial for mining and construction logistics. Kales offers specialized tipping semi trailers designed for robust performance on rough terrain.
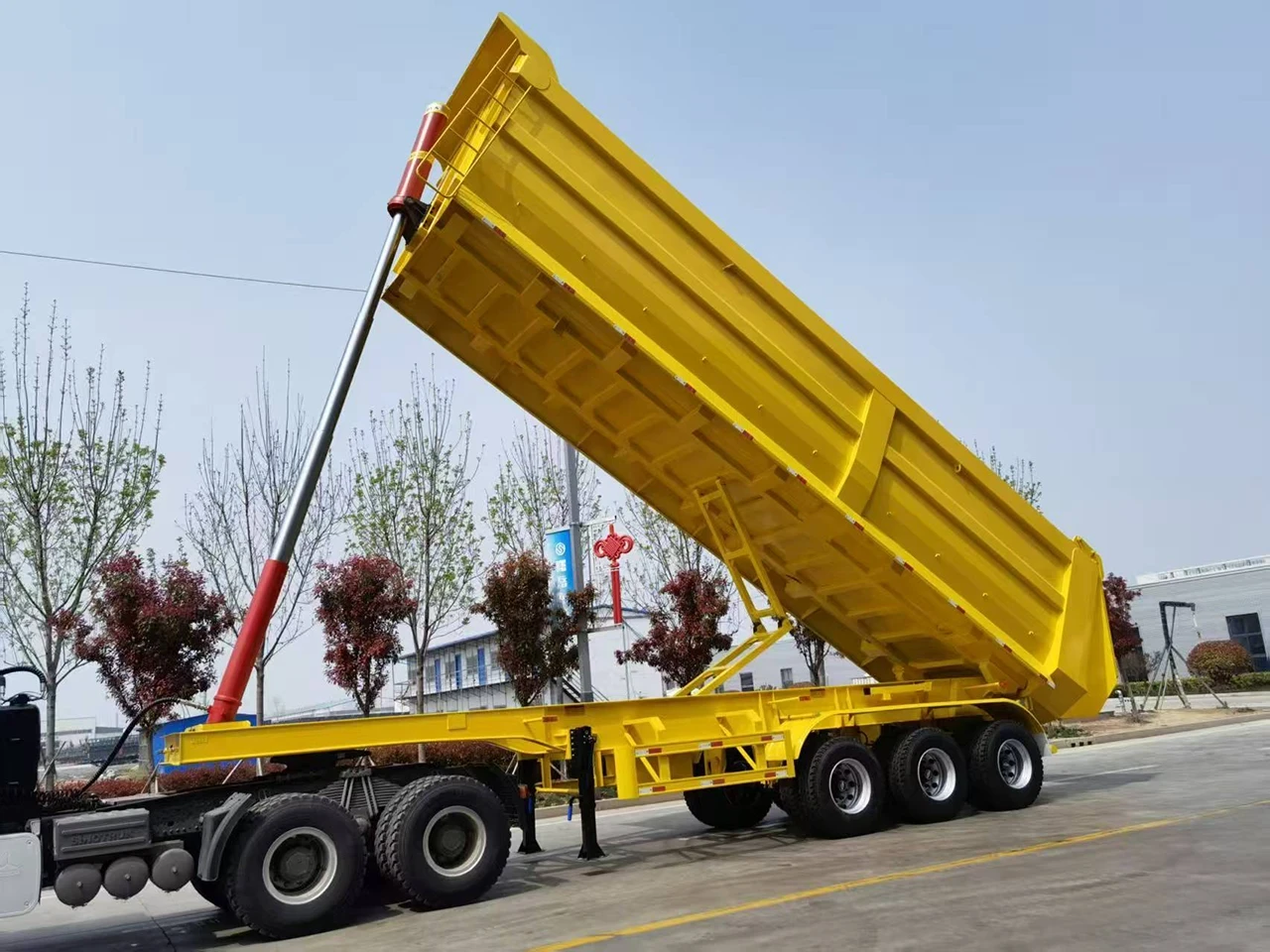
1.1 Rear Tipper Trailer (End Dump)
- Mechanism: The cargo box tilts backward, discharging material from the rear tailgate using a powerful telescopic cylinder.
- Best Applications: Mining transport, stone quarries, gravel yards, and heavy construction sites.
- Kales Features: Built with a heavy-duty chassis, front-mounted lifting cylinder, and a reinforced balance frame for superior stability during off-road operations.

1.2 Side Tipper Trailer (Side Tipping Semi Trailer)
- Mechanism: The body tilts to either the left or right side, ideal for efficient roadside discharge.
- Best Applications: Narrow railway projects, road construction, and sites with height limitations where a rear dump trailer cannot operate.
- Kales Features: Utilizes an advanced multi-cylinder synchronized tipping system. Precision hydraulic balancing ensures twist-free tilting even with uneven loads.

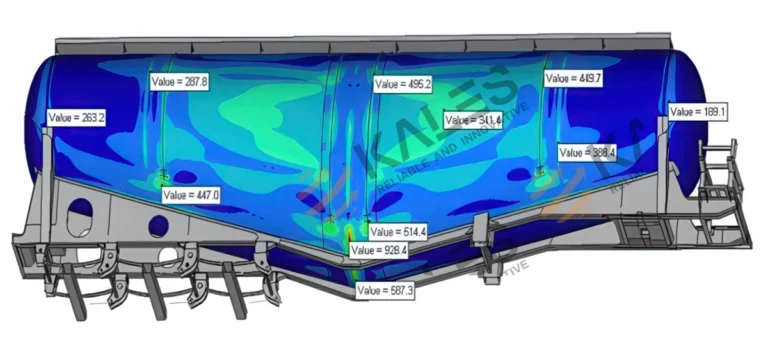
2. The Core: Kales Hydraulic Tipping System Explained
Kales tipper trailers rely on a mature high-pressure hydraulic system (~2.0 MPa), known for rapid response and precise lifting control under heavy loads.
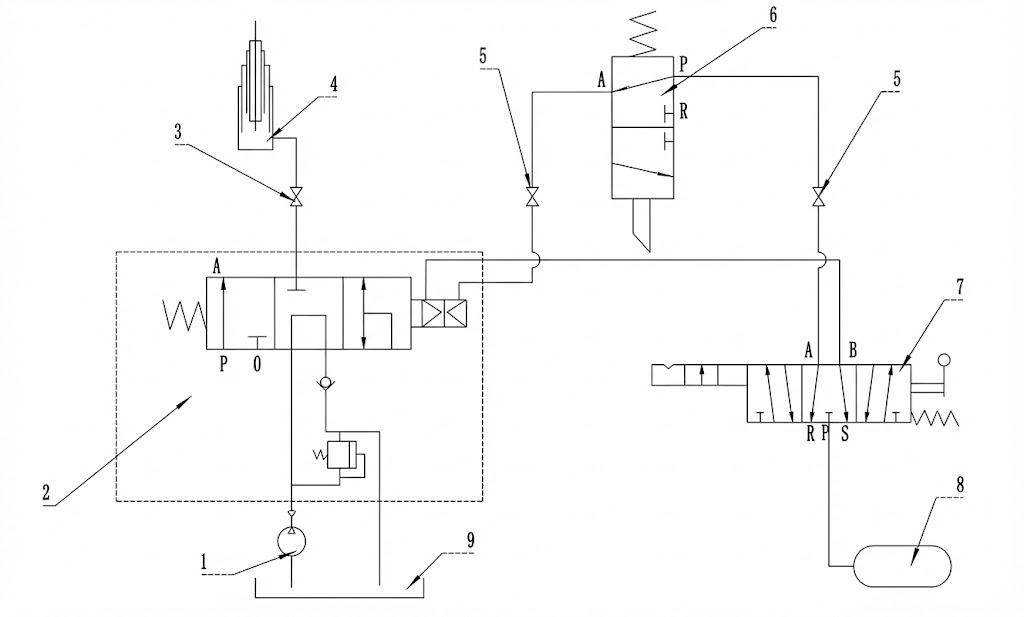
Rear Tipper Hydraulic Principle Diagram
1. Gear Pump (Hydraulic Power)
2. Pneumatic Control Valve
3. PTO (Power Take-Off)
4. Telescopic Lifting Cylinder
5. Quick Coupling Fitting
6. Limit Valve (Safety Stop)
7. Manual Cab Control
8. Air Source
9. Hydraulic Oil Tank
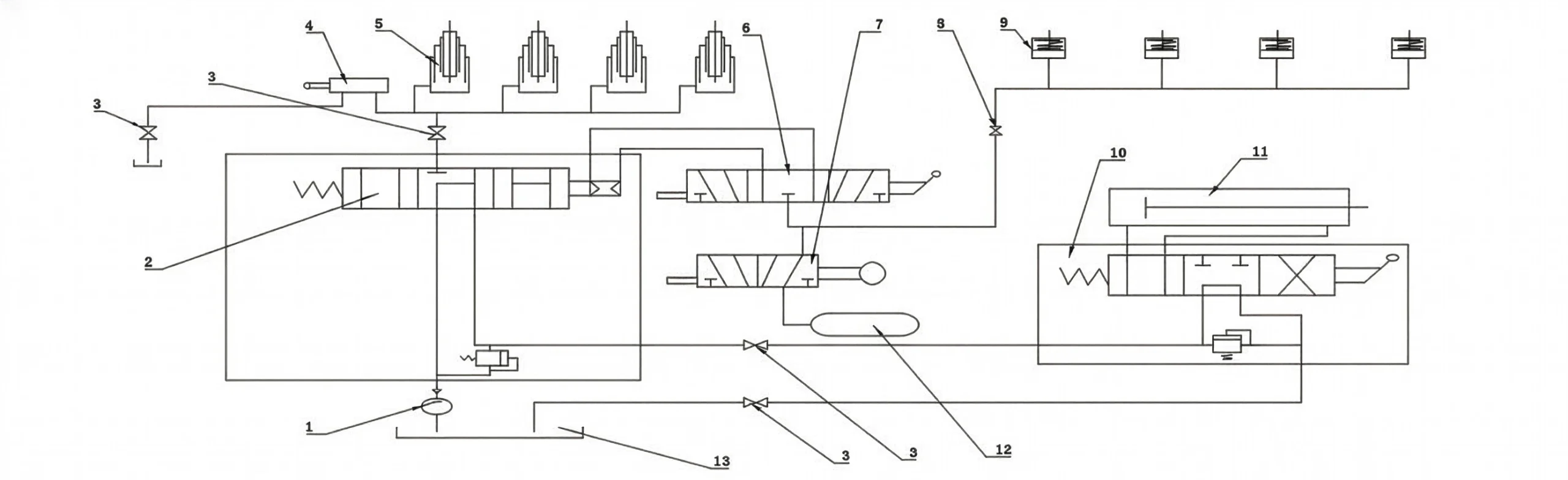
Side Tipper Hydraulic Principle Diagram
1. Hydraulic Pump
2. Directional Control Valve
3. PTO Unit
4. Hydraulic Limit Valve
5. Side Shift Cylinders
6. Tipping Control Valve
7. Side Door Locking Cylinder
8. Pneumatic Fitting
Key Hydraulic Components
- Power Unit (PTO Pump): Connects to the truck tractor gearbox to drive fluid flow.
- Control Unit (Valve Block): The “brain” of the tipping system.
- In-Cab Valve: Manual lever (Lift / Neutral / Lower).
- Limit Valve: Automatically stops the tipper body at max angle to prevent rollover accidents.
- Actuator (Hydraulic Cylinders): Hardened, chrome-plated cylinders designed for heavy-duty cycles and harsh environments.
3. Step-by-Step Operating Guide
- Park on solid, level ground (Slope ≤3°). Never dump on soft soil or uneven terrain.
- Engage the tractor parking brake completely.
- Ensure no overhead obstructions (power lines, bridges) typically found in construction zones.
3.1 Preparation (Side Tippers Only)
- Unlock the side gate using the pneumatic switch.
- Manually release any mechanical safety hooks on the cargo body.
- Check hinge pins: Ensure pins are locked on the correct side for discharge.
3.2 Lifting the Trailer Body
- Depress clutch pedal and engage PTO switch. Slowly release clutch.
- Move in-cab lever to “LIFT”.
- Gently increase engine RPM to control lift speed. Smooth operation prevents chassis stress.
- To pause: Disengage PTO and move lever to “Neutral”.
3.3 Lowering the Trailer Body
- Disengage PTO.
- Move control lever to “LOWER”.
- Gravity will lower the tipper box. Control descent speed by feathering the lever.
4. Troubleshooting: Tipper Hydraulic Faults
Use this guide to diagnose common issues with your tipping semi trailer.
| Symptom | Most Likely Cause | Quick Check Action |
|---|---|---|
| Tipper Won’t Lift | Electrical Issue (PTO) | Check fuse; Listen for solenoid “click” when engaging PTO. |
| Pneumatic Issue | Check truck air pressure; Check for blocked air lines to the valve. | |
| Hydraulic Issue | Check if Limit Valve is stuck. Check hydraulic oil level. | |
| Tipper Won’t Lower | Pneumatic Control Failure | Check air lines on the lowering side of the valve. |
| Slow Lifting Speed | Pump Wear / Air Leaks | Check engine RPM; Listen for air hissing; Check gear pump condition. |
| Body Vibration/Jitters | Low Hydraulic Oil | Stop immediately. Check oil tank sight glass to prevent pump damage. |
5. Maintenance Schedule & Lubricants
5.1 Hydraulic Fluid Specifications
| Climate Condition | Recommended Oil (ISO) | Performance Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Winter (Cold Regions) | L-HM 32 Anti-Wear | Low viscosity ensures fast flow during cold starts. |
| Summer (Hot/Tropical) | L-HM 46 Anti-Wear | High viscosity protects the pump in high-temperature environments (e.g., Africa/Middle East/SE Asia). |
5.2 Maintenance Checklist
- Daily: Check for leaks in hoses and the hydraulic tank. Verify PTO engagement.
- Weekly: Grease cylinder pins and tailgate hinges with Heavy Duty Lithium Grease.
- Monthly: Retorque structural bolts on the chassis frame.
- Every 6 Months: Drain tank, replace return filter, and refill with fresh hydraulic oil.
Need Spare Parts for Kales Tippers?
Keep your fleet running with genuine OEM parts for Kales Tipper Semi Trailers.